Subject
- #Blockchain-Based Contracts
- #Contract Automation
- #Digital Contracts
- #Smart Contracts
- #Blockchain
Created: 2025-03-23
Created: 2025-03-23 09:36
With the acceleration of digital transformation, traditional contract methods using paper documents or centralized servers are showing their limitations. As it becomes difficult to process complex transactions quickly and securely, blockchain-based contracts(smart contracts) are attracting attention.
Smart contracts execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met, leading to innovative changes in finance, real estate, public sectors, and more. Let's delve into the basic principles of smart contracts, real-world examples, implementation methods, security and legal issues, and future prospects.
Keywords: Blockchain, Smart Contract, Digital Contract, Contract Automation
A smart contract is an automatically executing contract written in codeon a blockchain.
For example, it can be set up so that money is automatically transferred when a specific date arrives.
This enables contract automationand real-time transaction processing, significantly reducing the role of intermediaries.
Keywords: Smart Contract, Blockchain-based Contract, Automation, Transparency
See the differences between traditional contracts and smart contracts in the table below.
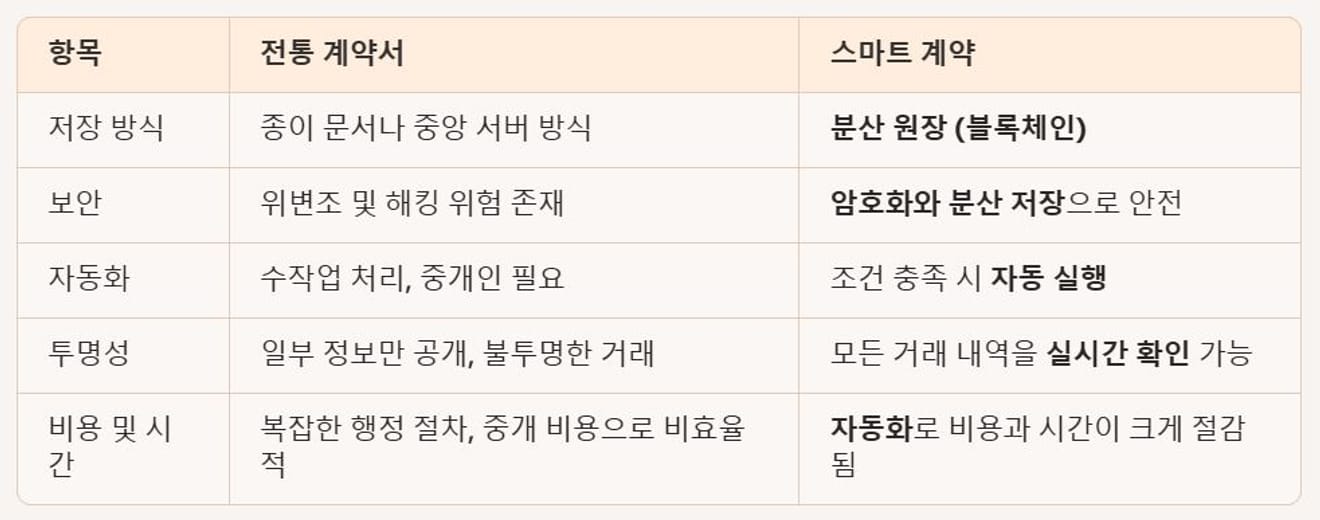
Comparison Table of Traditional Contracts and Smart Contracts
Keywords: Traditional Contract vs. Smart Contract, Digital Contract, Contract Automation

Traditional Contracts vs Smart Contracts
Finance and Insurance:
Many overseas financial institutions have adopted smart contracts to operate systems that automatically pay out when conditions such as loan approvals or insurance claims are met. This has significantly improved customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Real Estate Transactions:
The introduction of smart contracts has reduced paperwork and the role of intermediaries, significantly shortening transaction times and reducing brokerage fees.
Public Administration:
Government agencies are adopting blockchain-based systems for public procurement and contract signing to prevent corruption and make processing faster and more transparent.
Keywords: Financial Smart Contracts, Real Estate Blockchain Contracts, Public Administration Smart Contracts, Market Overview
1. Define Contract Terms:
Clearly define all the details, such as payment criteria, implementation schedules, and penalty clauses.
2. Code Writing:
Write the contract code in Solidity, the language primarily used on the Ethereum network.
3. Testing and Verification:
Check the code with various scenarios on a testnet (Ropsten, Rinkeby, etc.), and verify the execution results using tools like Etherscan.
4. Deployment and Maintenance:
After deploying to the mainnet, maintain system stability through regular security checks and updates.
Keywords: Smart Contract Development, Solidity, Testnet, Blockchain Implementation
Keywords: Smart Contract Security, Reentrancy Attacks, 51% Attacks, Security Audits
Smart contracts, in addition to their innovative advantages, have important issues regarding legal validityand regulation.
Many countries recognize the validity of smart contracts, but some use them in conjunction with traditional contracts. Governments and regulatory agencies are amending legislation to promote the use of blockchain technology, and are establishing legal standards through recent case law and expert opinions.
Keywords: Smart Contract Legal Validity, Blockchain Regulation, Recent Case Law, Legal Experts
Current Technological Limitations:
Future Integration Strategies:
Keywords: Blockchain Scalability, Layer-2, PoS, AI IoT Integration, Smart Contract Future
Field Interviews and Cases:
Adoption Effect Analysis:
Keywords: Smart Contract Cases, User Experience, ROI, Adoption Rate
Blockchain-based contracts overcome the limitations of traditional contracts and are an innovative solution optimized for the digital age through security, transparency, and automation.
Efficiency and reliability are increasing in finance, real estate, public sectors, and other fields through the adoption of smart contracts, and are expected to spread further in the future thanks to technological improvements and increased legal stability.
Keywords: Digital Contract, Blockchain-based Contract, Smart Contract, Future Technology
Comments0